Gene therapy viral vector assessment on retinal organoids
Tissue
Retina ModelsThe ask
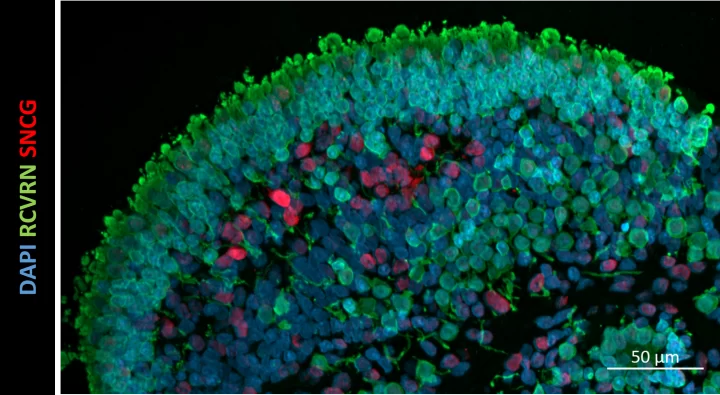
Our customer‘s goal was to rapidly evaluate a set of AAV constructs in vitro to compare their transduction efficiency and verify the cell types transduced in a neural retina model.
Our approach to developing a solution
We followed our standardised series of steps to develop a customised solution.
Step 1:
UNDERSTANDING THE PROBLEM
We clearly defined the problem and questions to be answered through in-depth discussion between the customer and our technical experts.
The customer wished to compare the transduction efficiency of a series of AAV vectors with different capsids, promoters and transgenes.
Taking all project specific factors into account, we suggested a two-step approach as being the most appropriate for their situation:
- Step 1: Optimise the transduction of retinal organoids with AAV vectors
- Step 2: Detailed imaging analysis and constructs comparison
Step 2:
DEVELOPING A CUSTOMISED EXPERIMENTAL PLAN
We designed the specific experiments and presented the plan in our Statement of Work.
Our experimental plan involved using fully validated human retinal organoids.
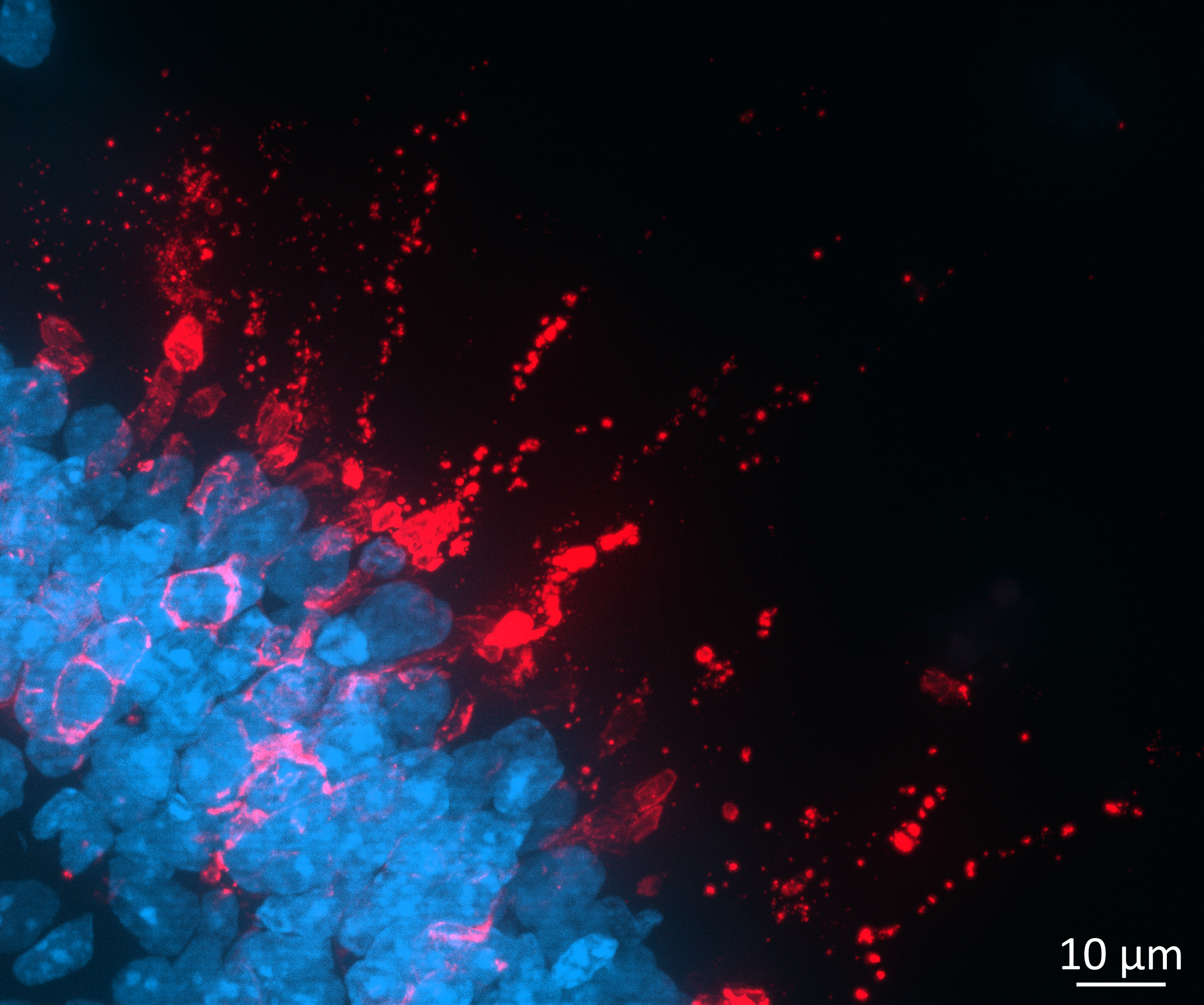
For Step 1, Organoids were transduced at day 150 of differentiation with AAV vectors and live imaging was performed from 5 to 27 days post-transduction.
- The experiments aimed to evaluate the transduction efficiency of the various AAV constructs.
- We also checked organoid viability was not negatively affected by AAV transduction.
For Step 2 we planned to carry out the following imaging analysis,:
- Quantification of the % of cells expressing the transgene
- Verify the nature of the transduced cells, namely photoreceptors by co-localisation studies
Step 3:
PROJECT EXECUTION
Our scientists carried out the agreed experiments within 3 months providing regular updates to the customer.
The study included the experimental phase, data processing, data analysis and presentation of a data summary.
Example dataset
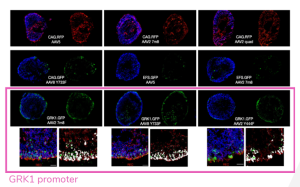
Imaging comparison of a series of AAV construct with different promotors, reporter genes and capsids.
Step 4:
RESULT DELIVERY
We delivered a detailed report with reliable dataset which was shared digitally and discussed over a call upon request.
The study clearly showed :
- Transgene expression in photoreceptors post transduction was the highest when the transgene was under the control of the rhodopsin kinase GRK1 promotor reaching 5 % of cells with all capsid variants.
- Transduction of photoreceptors by confirming co-localisation of the transgene and recoverin by immunostaining.
This study expanded the options of AAV capsid and transgene to be used for preclinical testing of gene therapy to include CAG quad mutant variants and GRK1 into AAV vectors
Outcomes for the client
We delivered a robust dataset which clearly showed that human retinal organoids are a robust in vitro model for rapid screening of AAV constructs. Our analysis gave confidence to our customer to select the most effective AAV construct.