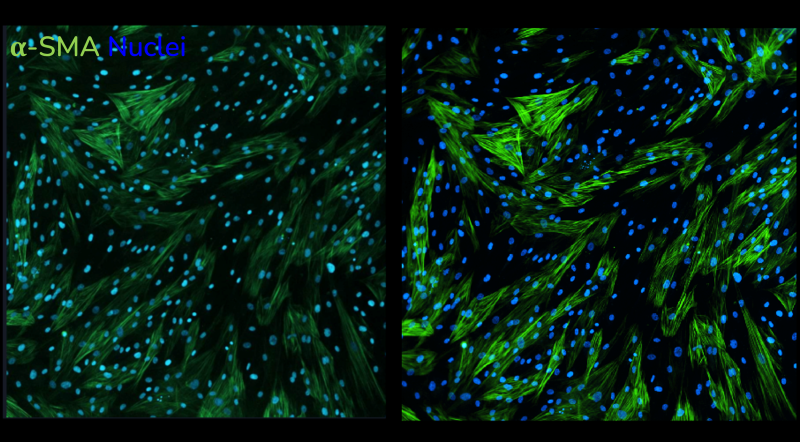
High-throughput in vitro assessment of fibroblast-to-myofibroblast (FMT) transition using high-content imaging
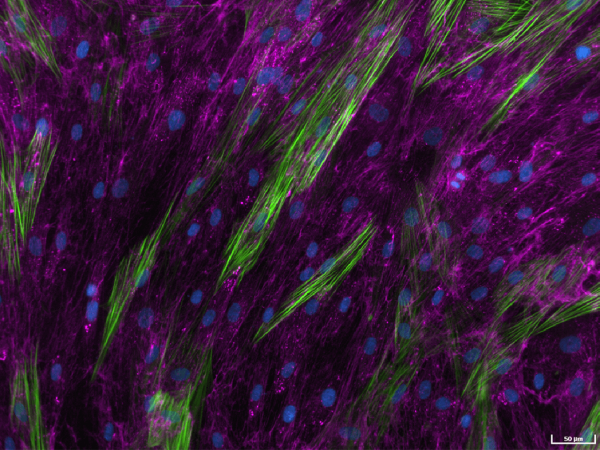
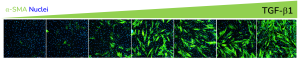
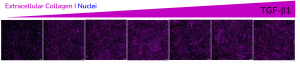
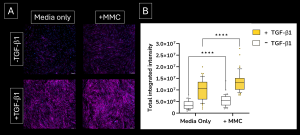
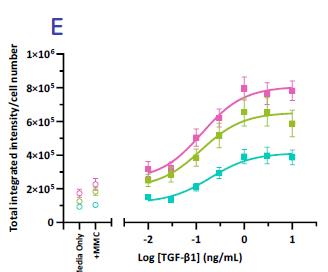
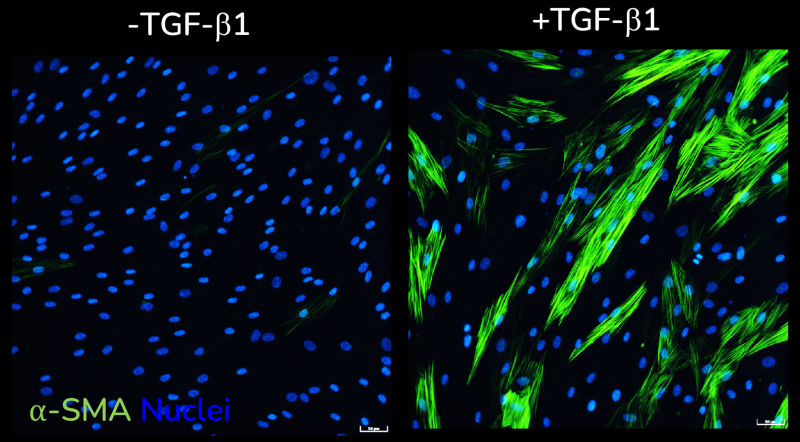
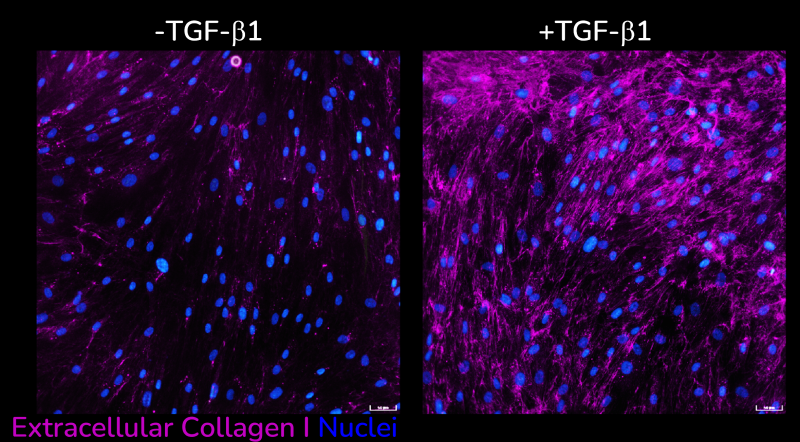
The high-throughput, high-sensitivity FMT assay has been specifically designed to accurately and rapidly study a compound’s ability to prevent lung fibroblast activation and reduce the deposition of extracellular matrix proteins following stimulation with the well-established fibrotic mediator TGF-β1.
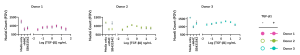
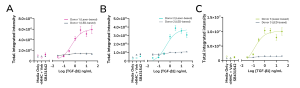
Our assay setup allows for advanced testing of small molecule drugs at multiple concentrations.
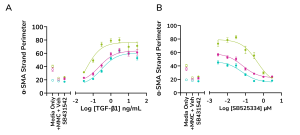
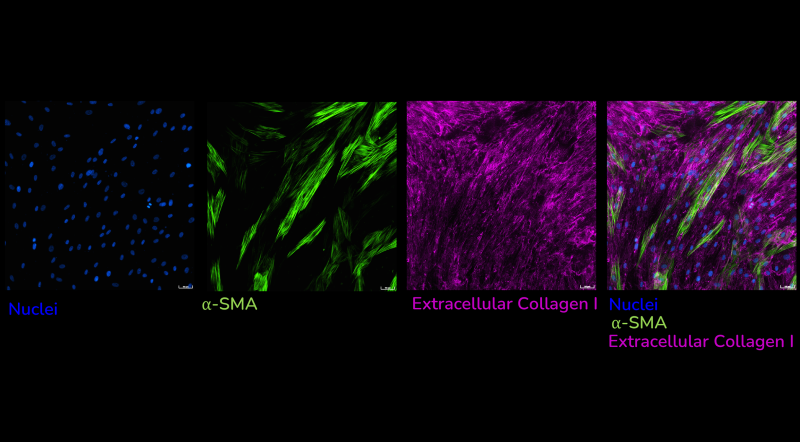
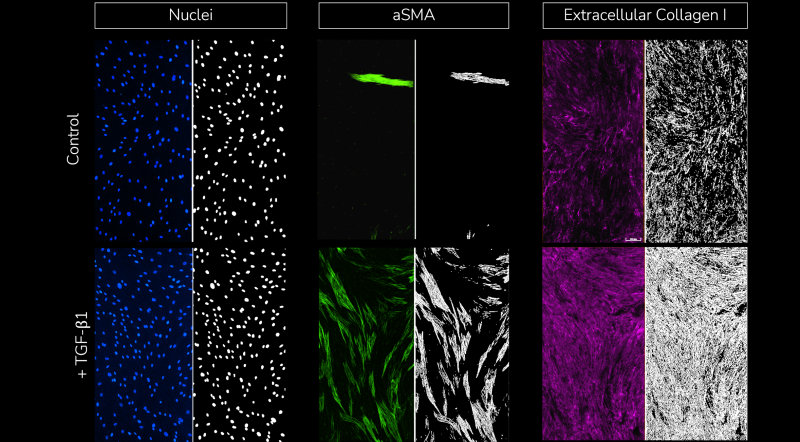
Using multiplexed detection, this FMT assay provides the accurate data needed to advance drug-discovery programs by determining changes in cell count, α-SMA expression, α-SMA strand perimeter and extracellular collagen I deposition.
The rapid, high-throughput fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition (FMT) assay service leverages our state-of-the-art imaging suite capabilities to accurately evaluate the efficacy of anti-fibrotic compounds with fibrosis-related marker readouts. Automatic quantification and analysis ensures objectiveness in data quality.
FMT Assay service outputs
- Cell count
- Automated quantification and analysis of extracellular collagen I deposition
- Automated quantification and analysis of α-SMA expression
- Automated quantification and analysis of α-SMA strand perimeter