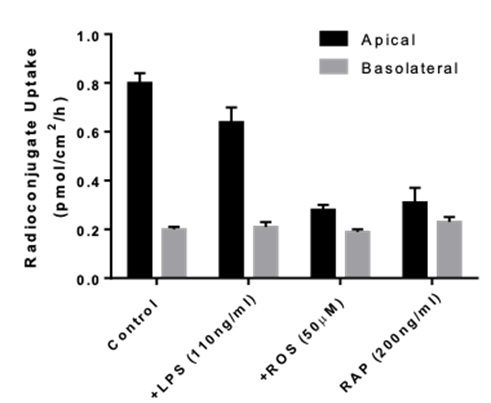Investigate renal drug transport modalities and drug interactions in vitro
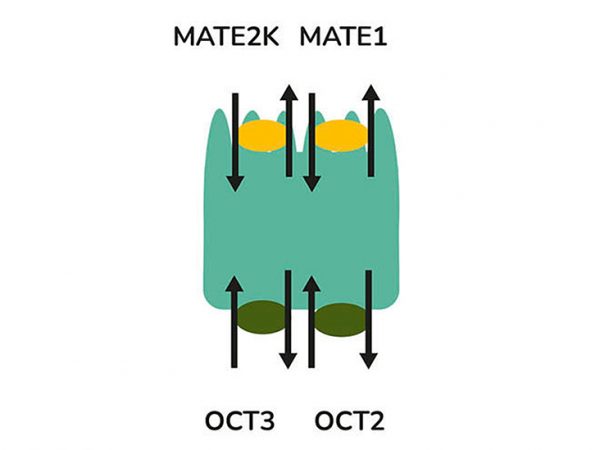
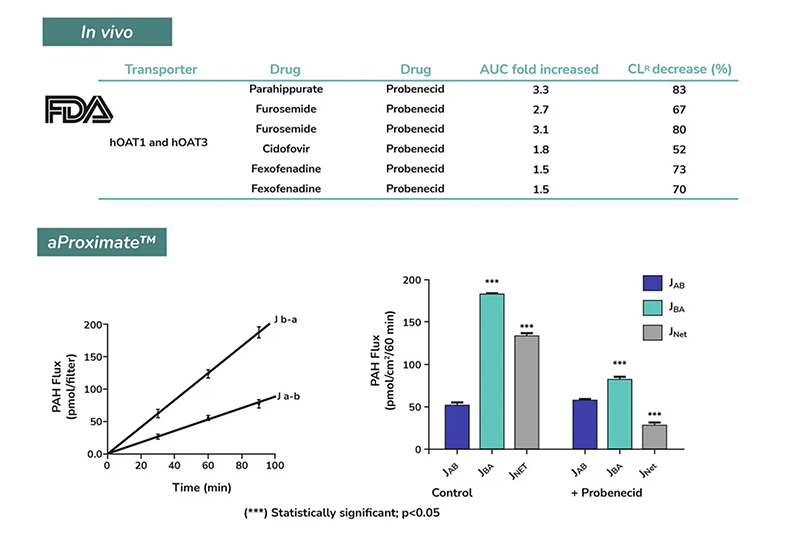
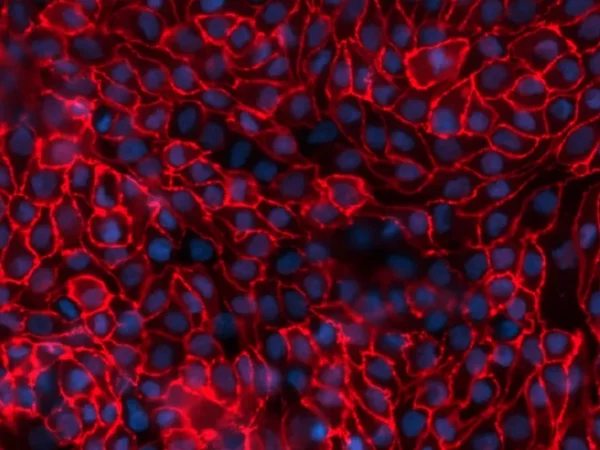
aProximate™ PTCs retain high expression of the relevant transporters involved in drug handling including megalin and cubilin; so are ideal for drug transporter and drug interaction studies of both small and large molecules. Transporters play a major role in the uptake and efflux of drugs across cellular membranes. Drug interactions with transporter proteins are common and can act either as substrates and/or inhibitors, a role which is best be identified during the early-stages of drug development to define the absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME) profile. Using our scientific expertise, Newcells provides transporter assays using the aProximate™ model to support your specific requirements and understand potential drug interactions.
“I have had a very positive experience working directly with the Newcells team using their aProximate™ complex in vitro kidney model in support of several drug transport projects. This model is the only one that can present elusive organic anion transporter (OAT1, OAT2, OAT3) functionality above and beyond the commonly reported organic cation transporter (e.g., OCT2, MATE1/2K) activity of other models. This has enabled careful characterization of the transporters (OCT2 versus OAT2) involved in the secretory renal clearance of creatinine, a widely used biomarker of renal function in clinical studies (J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2024 Jan 2;388(1):201-208).” David Rodrigues, PhD, ADME expert
Service outputs
- Flux Assay: Apical to Basal (Jab) and Basal to Apical (Jba) flux
- Net transport measurements
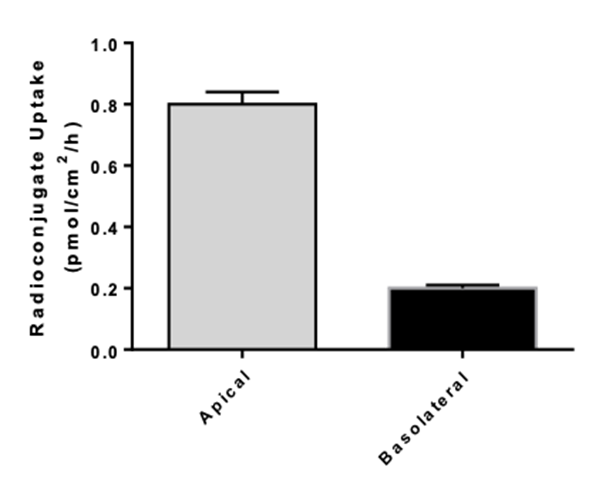
- Uptake assays : measurement of intracellular drug and metabolite concentrations
- Identification of transporter-mediated drug interactions
- High content imaging data